How Do You Become An Electrical Engineer?
Electrical engineering is a vast field – covering a variety of concentrations such as multimedia, communications, energy, biosystems, consumer electronics, control systems and RF engineering, among others. If you want to become an electrical engineer, you could be working on anything from small handheld devices to massive electrical grids.
If you are interested in this field, the career you end up in would depend largely on your preferences, experience and most importantly, your educational qualifications.
The following guide is meant to serve as a useful resource for aspiring electrical engineers. It covers the duties of an electrical engineering, steps to become an electrical engineer, educational requirements, salaries and projected growth in the field.
Featured Programs and Schools
Duties of an Electrical Engineer
Electrical engineers design, develop and test various kinds of electrical equipment. They also supervise the operations and ensure that all systems are running smoothly. Equipment they work with could include electric motors, navigation systems, communications systems or power generation machinery.
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, electrical engineers have the following duties:
- “Design new ways to use electrical power to develop or improve products
- Perform detailed calculations to develop manufacturing, construction, and installation standards and specifications
- Direct the manufacture, installation, and testing of electrical equipment to ensure that products meet specifications and codes
- Investigate complaints from customers or the public, evaluate problems, and recommend solutions
- Work with project managers on production efforts to ensure that projects are completed satisfactorily, on time, and within budget”
Select Your State
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indian
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Types of Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering uses the principles and theories of electricity, electromagnetic field theory and electronics. The field has been divided into many categories because of the diversification and innovations in each sub-field. The most common types of electrical engineering are as follows:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Engineering | Deals with power related issues such as the production, transmission, distribution and use of electricity. |
| Telecommunication Engineering | Deals with the transmission of information via cellular systems. |
| Electronics Engineering | Deals with the design and operation of electronic devices, circuits and electronic systems. |
| Mechatronics Engineering | Deals with a combination of electronic, computer, mechanical, telecommunications and control engineering. |
| Avionics Engineering | Deals with the designing and operation of systems such as rockets, aircrafts and space shuttles. |
| Biomedical – Electronics Engineering | Deals with electronics in the field of medicine such as MRI and X-Ray machines, artificial limbs and hearts etc. |
| Nuclear Engineering | Deals with the mining and processing of nuclear materials, along with waste management, extraction and immobilization methods. |
| Photonics Engineering | Deals with generating, processing and detecting light (photons) which carries useful information such as voice telephony, image data files or measurement signals etc. |
Career Outlook and Salary for Electrical Engineers
Electrical engineers earned a mean annual wage of $101,600, as per May 2018 data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. The employment in this category was 186,490. The industry with the highest level of employment in this sector was Architectural, Engineering and Related Services, with a total of 39,860 people working. The highest concentration of employment was in Electric Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution. The top-paying industry for electrical engineers was Oil and Gas Extraction, with an annual mean wage of $126,610.
Job growth for electrical engineers is expected to be mainly in engineering service firms and organizations working on the development of sophisticated consumer electronics. The rapid rise in technological innovation is expected to drive the demand for electrical engineers in research and development. Engineers are also expected to play an important role in development of technologies such as solar arrays, communication systems and semi-conductors.
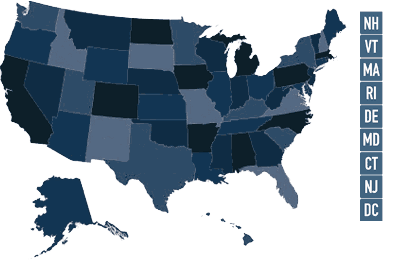
Best States for Electrical Engineering
As per the data from US Bureau of Labor Statistics for May 2018, California had the highest level of employment in this category with 26,570 people employed, followed by Texas (14,680), New York (10,500), Michigan (9,190) and Pennsylvania (8,870). The top paying states for electrical engineers were Alaska, with an annual mean wage of $119,130, followed by New Jersey ($118,120), District of Columbia ($118,000), Maryland ($116,560) and Vermont ($115,460).
Steps to Become an Electrical Engineer:
- Get a bachelor’s degree or higher
The entry-level education for electrical engineers is a 4-year long bachelor’s degree, accredited by the ABET – Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology. The coursework in this degree would typically include electrical circuit theory, digital systems design and differential equations. Electrical engineering programs would include classroom, laboratory or field studies. Some colleges also offer cooperative programs where students can get practical experience while completing their degree. Internships also provide similar experience opportunities.
In addition to this, there are also universities that offer a 5-year program which leads to both, a bachelor’s degree and a master’s degree.
- Pass the Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam
Electrical engineers who wish to work in the utility field need to get licensed through the Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) exam. Students who get a passing grade on this exam are then referred to as engineers-in-training (EITs) or engineer interns (EIs) until they pass the Professional Engineer (PE) exam.
- Gain experience and/or get a graduate degree
Advancing in this field requires that you either get experience or go for a graduate program to add to your skill set. A graduate degree can help you fast track your advancement as an electrical engineer.
- Pass the Professional Engineering Exam
To qualify for this exam, EITs need to have at least four years of relevant work experience. In addition to this, several states have continuing educational requirements for professional engineers in order to retain their licensure.
Should You Become an Electrical Engineer?
Electrical engineering is a field with bright future prospects. There are multiple reasons why you ought to become a part of this industry.
- Varying work environments
Electrical Engineers are required to work in offices, on-site, in labs and at power plants etc. The varying work environments helps break the monotony associated with a desk job.
- Opportunities to travel
Electrical engineers travel to various places for their projects and that is another positive if you are someone who enjoys travelling.
- Job security
Even though the industry is always on the lookout for fresh mindset, there is always a demand for experienced professionals.
- Solid growth rate
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the growth for electrical and electronics engineers, between 2016 and 2026, is expected to be around 7%, which is as fast as the average growth for all occupations. 21,300 jobs are expected to be added in this category during this time period.
- Decent salaries
Electrical engineers typically earn high salaries, depending on their education and experience.